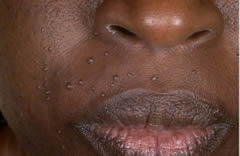
A healthy 40-yo woman on no meds originally from sub-Saharan Africa c/o 5 mo of itchy papules around her mouth. Exam showed a cluster of pearly papules. What is it?
|
Milia
|
|
Acne vulgaris
|
|
Folliculitis
|
|
Herpes simplex
|
|
Molluscum contagiosum
|
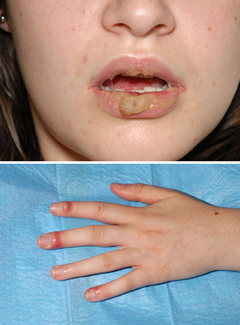
A young woman presented with lesions on her lips, tongue, and oral mucosa. Finger lesions and low-grade fever began a few days after the oral lesions. What is it?
|
Coxsackie virus
|
|
Impetigo
|
|
Herpes simplex
|
|
Kawasaki disease
|
|
Behcet's disease
|
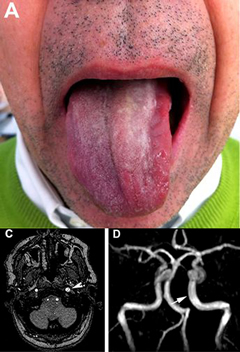
A 54-yo man with mild HTN on no meds c/o of dysarthria, trouble with swallowing and moving his tongue. Neuro exam was normal except for left-side tongue deviation. Blood work excluded infection or immune disorders. An MRI was performed. What is it?
|
Multiple sclerosis
|
|
Complicated migraine
|
|
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
|
|
Carotid artery dissection
|
|
Acute cerebral vascular occlusion
|
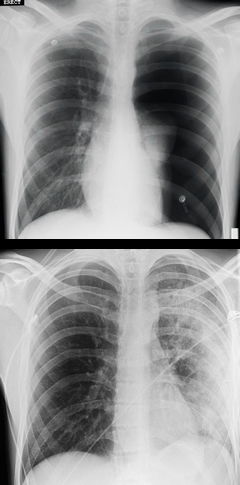
(BMJ) - A 19-yo man with no PMHx had a chest tube placed for a large spontaneous pneumothorax. Symptoms initially improved, but soon he began coughing up frothy, clear, yellow, sputum and developed respiratory distress. X-ray was repeated. What is the diagnosis?

|
Reexpansion pulmonary edema
|
|
Chest tube malfunction
|
|
Lung abscess
|
|
Atypical pneumonia
|
|
Pulmonary hemorrhage
|
(BMJ) - A 74-yo man with no past medical Hx c/o pain and blisters on his right hand several hours after playing hockey. There was no trauma to his hands. He had no fever or other symptoms. What is the diagnosis?
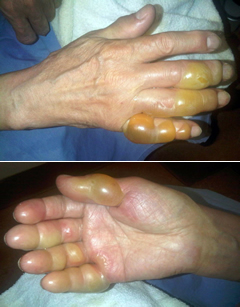
|
Allergic reaction
|
|
Flexor tenosynovitis
|
|
Herpes zoster
|
|
Blistering distal dactylitis
|
|
Frostbite
|
(BMJ) - A 40-yo man c/o nasal blockage x 11 yrs, anosmia, and “something coming out of my nose.” Hx includes hay fever and aspirin intolerance. Exam revealed bilateral glistening fleshy structures in his nose, left worse than right. What is the diagnosis?
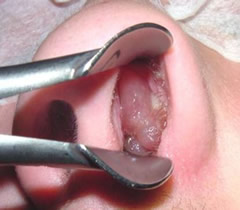
|
Septal hematoma
|
|
Deviated septum
|
|
Nasal foreign body
|
|
Rhabdomyosarcoma
|
|
Gross nasal polyps
|
